India has a distinctive tax structure which has evolved over a period of time. Most of the business taxation is levied by the state governments. The major part of reforms in the Indian taxation system have happened in the last decade or so. The overall tax system has been rationalized to ensure, that businesses can pay taxes with ease and more tax revenue can be generated.
Here are some of the important taxes that Indian businesses have to deal with:
Central Sales Tax
If a dealer of goods sells his goods outside of the state, then this tax is applicable. Central Sales tax is generally payable on the sale of all goods by a dealer in the course of inter-state trade or commerce or, outside a state or, in the course of import into or, export from India.
Value Added Tax
All goods go through various levels in the process of production and supply chain. Value added tax is a tax levied on goods, at each level of the supply chain. The state sales tax has now been replaced by the VAT and this is one of the more significant tax reforms in recent times.
Some of the key features of Value added tax in India include:
Most of the Value Added tax rates are common for all the Union territories and states in the country.
The basic rates of VAT are 4% and 12.5%, while some of the services are excluded and have a special rate of 1%. Some basic commodities also have a VAT rate of zero percent.
With the new reforms all the state taxes can be converted to VAT. VAT however, does not cover the inter state transactions. All purchases made with respect to exports is exempted from taxes. The whole process has been made more business friendly by facilitating self assessment for dealers.
Dealer with a sales turnover of less than Rs. 5 lakh are exempted from VAT need not register themselves for VAT.
Excise Duty
Manufactured goods in India are charged with a tax called the Central Excise Duty. The specified goods unders the act come under this tax. There are 3 specific types of excise duties:
Basic Excise Duty
This is a tax charged on all the goods produced in the country. The tax is applicable on all goods other than salt.
Additional Duty Of Excise
This taxes is collected for goods that are mentioned in the Section 3 of the Additional duties of Excise (goods of special importance) Act, 1957.
Special Excise Duty
This duty is levied as per the section 37 of the Finance Act of 1978.
Customs Duty
This duty is levied on import of goods. The rate of taxation depends on their classification. Over the years the peak customs duty has been reduced to rationalise the taxation system.
Choosing the right online invoicing solution would help Indian businesses to manage their taxation with ease. Online solutions have the following business advantages:
- Improves the efficiency of the invoicing system
- Helps in sending out invoices online, saving on paper costs
- Helps in getting paid quicker with online payments
- Customizing the invoicing according to client requirements
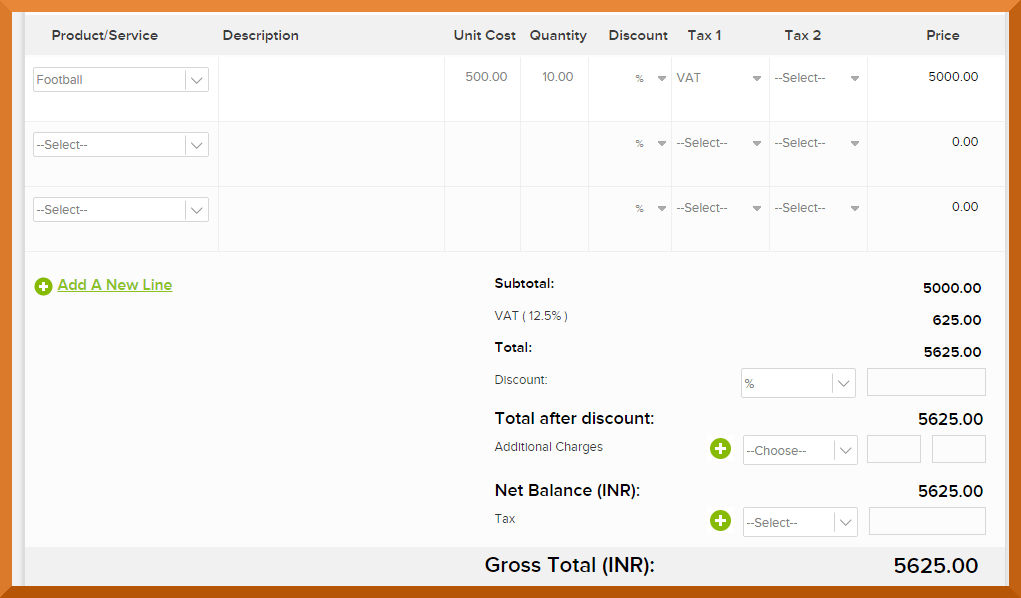
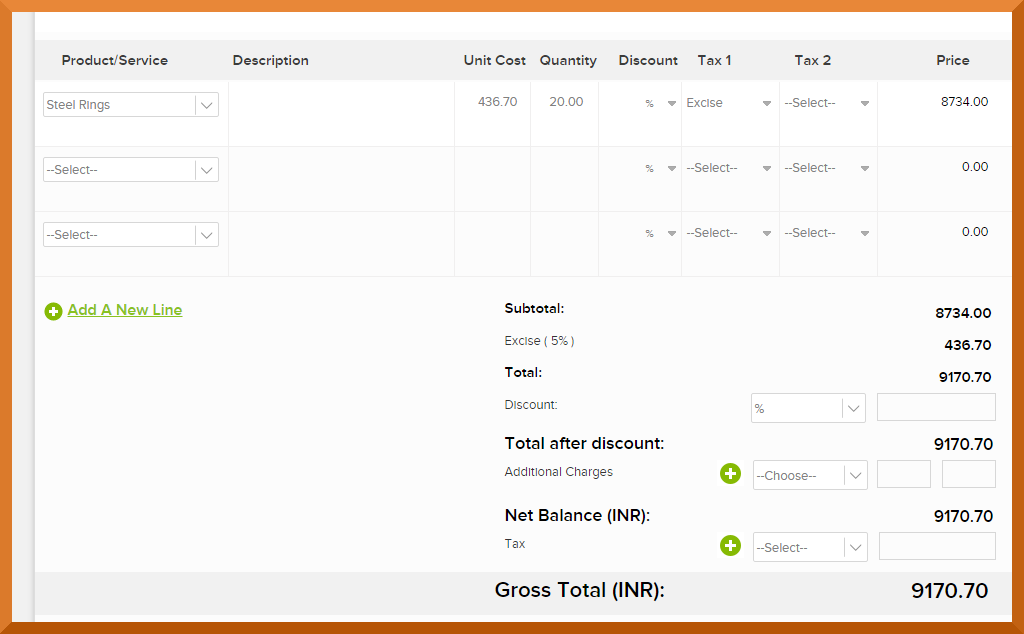
Invoicera is one such billing software that helps in managing the invoicing requirements of small and large businesses with ease. The software provides a simple option of additional fields, that helps in adding any state or central tax with ease. Multiple currencies and payment gateways ensure that if a business has global clients, then they too can be managed well.
Some of its other features include:
- Late fee and automatic payment reminders
- Time tracking and task management
- Expense management and control
- Advanced reporting and financial management
- Time tracking and time billing management
- Expense tracking and expense billing management
- Recurring billing management
- Project and task management
- Receive online payments
- Purchase order management